What are the Manufacturing Processes of Forged Steel Valves?
What are the Manufacturing Processes of Forged Steel Valves?
Forged steel valves are different from ordinary cast steel valves, which leads to the difference in performance between the two types. This article introduces the manufacturing process of forged steel valves and makes a comparison with cast steel process for reference.
Forging Steel Process
Forged steel refers to various forgings produced by forging process. The quality of forged steel components is superior to that of cast steel parts, which can withstand large impact loads. Its plasticity, toughness and other mechanical properties are also better than cast steel parts. Therefore, forged steel parts shall be adopted for some important mechanical components.
Forged steel is usually applied to high-pressure pipelines with a compact internal structure, which is suitable for high-pressure working conditions, such as forged steel ball valves, forged steel globe valves, forged steel gate valves and other high-pressure & high-temperature forged steel valves.

Classification of Forging Process
Closed Die Forging (Die Forging)
It is divided into precision forging, rotary swaging, cold heading, extrusion and other processes. The metal billet is placed in a forging die with a specific shape and pressed to deform, so as to obtain the finished forging.
According to the deformation temperature, it is classified into:
Cold forging (Forging temperature at room temperature)
Warm forging (Forging temperature lower than the recrystallization temperature of the billet metal)
Hot forging (Forging temperature higher than the recrystallization temperature)
Open Die Forging (Free Forging)
It includes manual forging and mechanical forging two ways. The metal billet is placed between the upper and lower anvils, and the shape of the metal billet is changed by impact force or pressure to obtain the required forgings.
Core Advantages of Forging Process
Forging is one of the core processes for manufacturing high-quality valve components. Most important components of machinery under high load and severe working conditions are forgings, except for simple-shaped welded parts made of section plates.
Through the forging process, the blowholes and as-cast porosity of metal materials can be eliminated effectively. The correct selection of forging ratio is of great significance to improve product quality and reduce production cost.
Key Parameters of Forging Process
Main Forging Materials: Carbon steel, stainless steel and alloy steel
Forging Ratio: Refers to the ratio of the cross-sectional area of metal before deformation to that after deformation
Raw Material State: Ingot, bar, liquid metal and metal powder
The mechanical properties of forgings are generally better than those of castings made of the same material. Forging is a process that applies plastic pressure to metal billets through forging machines to make the metal billets produce plastic deformation, so as to obtain the shape and size with excellent mechanical properties.
Comparison between Forged Steel and Cast Steel
Cast Steel Basic Introduction
Cast steel refers to steel used for casting castings, a type of casting alloy. It is divided into cast carbon steel, cast low alloy steel and cast special steel. Cast steel parts are produced by casting process, which is mainly used to manufacture components with complex shapes that are difficult to forge or cut, and require high strength and plasticity.
Core Differences & Defects
Cast steel has obvious defects such as large blowholes and loose internal structure, and its overall strength is far inferior to forged steel.
Conclusion: For this reason, forged steel valves are mainly used in the high-pressure, high-temperature and key important positions of industrial pipelines.
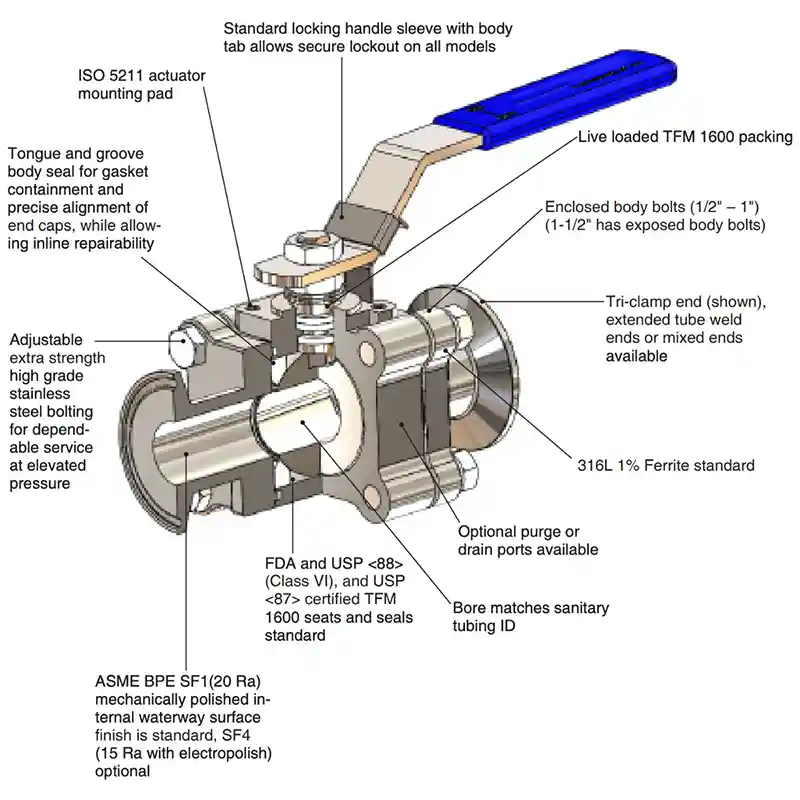 How to operate a sanitary ball valve?
How to operate a sanitary ball valve?
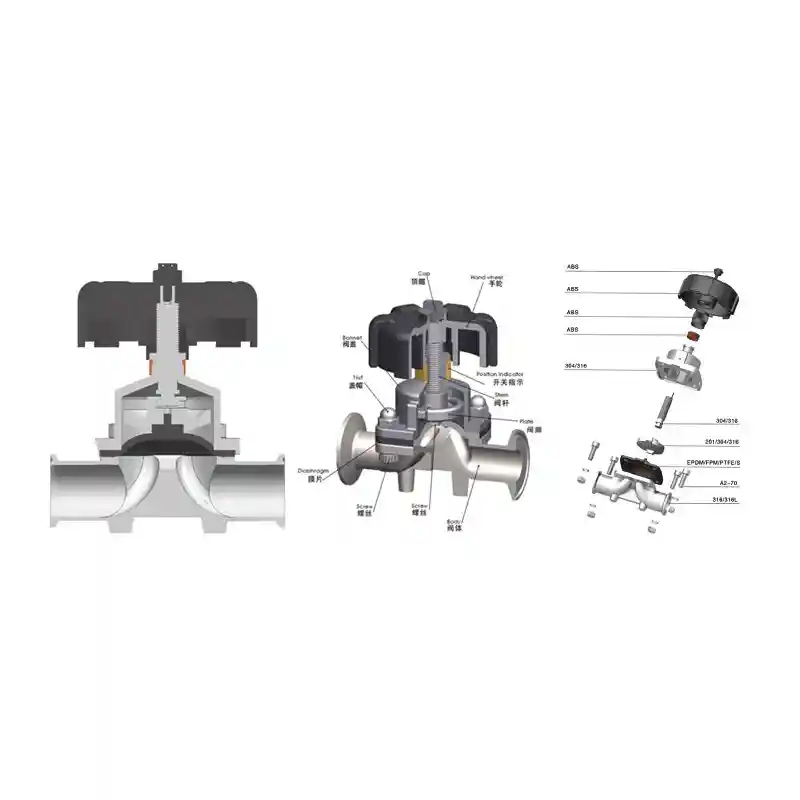 How to Correctly Use Stainless Steel Sanitary Diaphragm Valves?
How to Correctly Use Stainless Steel Sanitary Diaphragm Valves?
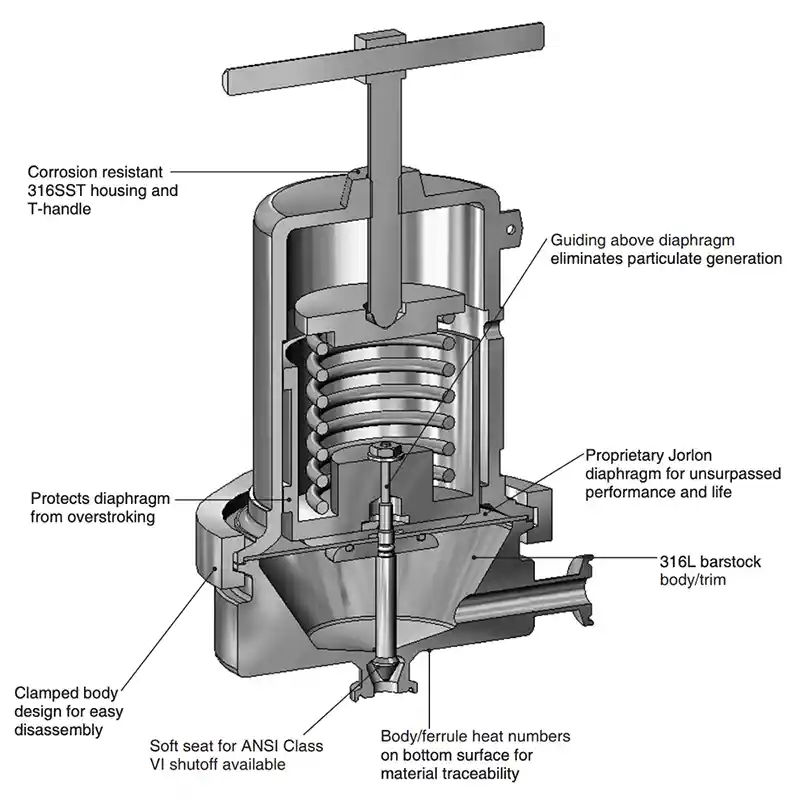 What is a Sanitary Pressure Regulator?
What is a Sanitary Pressure Regulator?
 What Are Sanitary Valves?
What Are Sanitary Valves?




